Coronal Section Across the Foramen of Monro and Apex of the Insula Neuroanatomy The
A good understanding of the anatomy of the foramen of Monro is essential for the neurosurgeon, especially with the increasing use of intraventricular endoscopy.

7Brain VentriclesForamen of MonroCSFChoroid PlexusNeural Control & CoordinationNEETClass
The foramen of Monro lies at the junction between the paired lateral ventricles and the third ventricle of the brain. A comprehensive review of the literature was performed focusing on the foramen of Monro. A good understanding of the anatomy of the foramen of Monro is essential for the neurosurgeon, especially with the increasing use of.

Measuring the dimensions of the Foramen of Monro. In this example, the... Download Scientific
Conclusions: A good understanding of the anatomy of the foramen of Monro is essential for the neurosurgeon, especially with the increasing use of intraventricular endoscopy. Original language: English: Pages (from-to) 1645-1649: Number of pages: 5: Journal: Child's Nervous System: Volume: 30: Issue number: 10:

Standard Endoscopic Vision of the Right Foramen of Monro Download Scientific Diagram
The Foramen of Monro is a pair of small openings that connect the lateral ventricles of the brain to the third ventricle. It serves as a channel through which cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) flows, aiding in the maintenance of intracranial pressure and the nourishment of brain tissue. Imaging the Foramen of Monro MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging)
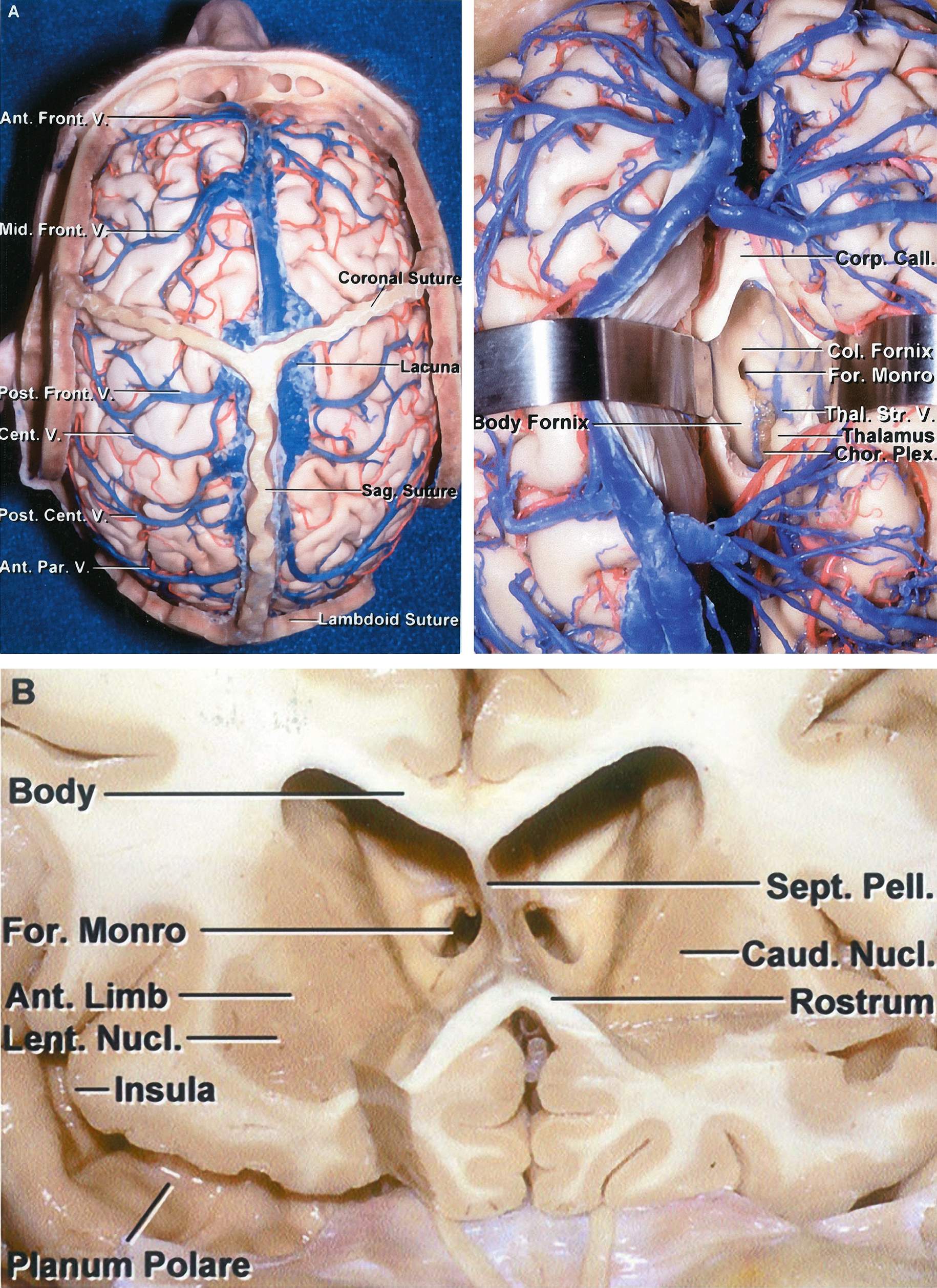
External Ventricular Drain The Neurosurgical Atlas
The interventricular foramen (aka Foramen of Monro) is a short passage extending from the lateral ventricle to the third ventricle, allowing for the drainage of cerebrospinal fluid from the lateral ventricles to the third ventricle. Complete Anatomy The world's most advanced 3D anatomy platform Try it for Free

Foramen Monroi Ars Neurochirurgica
The foramen of Monro is a short conduit between the paired lateral ventricles and the third ventricle of the brain. This deep structure becomes clinically significant when obstructed and leads to obstructive (non-communicating) hydrocephalus.

Figure 5 from Colloid cysts posterior and anterior to the foramen of Monro Anatomical features
The interventricular foramen, also known as foramen of Monro , is part of the ventricular system and the connection between the third ventricle and the lateral ventricle .

Foramen The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary
In the brain, the interventricular foramina (or foramina of Monro) are channels that connect the paired lateral ventricles with the third ventricle at the midline of the brain. As channels, they allow cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) produced in the lateral ventricles to reach the third ventricle and then the rest of the brain's ventricular system. The walls of the interventricular foramina also.

14 Foramen monro immagini, foto stock e grafica vettoriale Shutterstock
The foramen of Monro is an oval-shaped cylinder that changes in size and orientation in the hydrocephalic patient. If universally applied to all patients regardless of foramen and tumor size, ETV/biopsy can displace structures around the Foramen of Monro up to 1 cm, which can potentially lead to neu.

Occlusion of one Monroi foramen leads to unilateral hydrocephalus.... Download Scientific Diagram
The differential diagnosis of masses arising from the foramen of Monro can be approached depending on the age of the patient. Pediatric choroid plexus papilloma adamantinomatous craniopharyngioma germinoma glioma Langerhans cell histiocytosis neurofibromatosis pilocytic astrocytoma subependymal giant cell astrocytoma Adult aneurysm colloid cyst

Image result for foramen of monro and luschka Cerebrospinal fluid, Spinal cord, Anatomy
Abstract. Alexander Monro "Secundus" (1733-1817) was, according to Guthrie, born to greatness. His grandfather John Monro (1670-1740), who had studied medicine at Leyden under his fellow Scot Archibald Pitcairne (1652-1713), became one of the protagonists of the foundation of a medical school at Edinburgh.
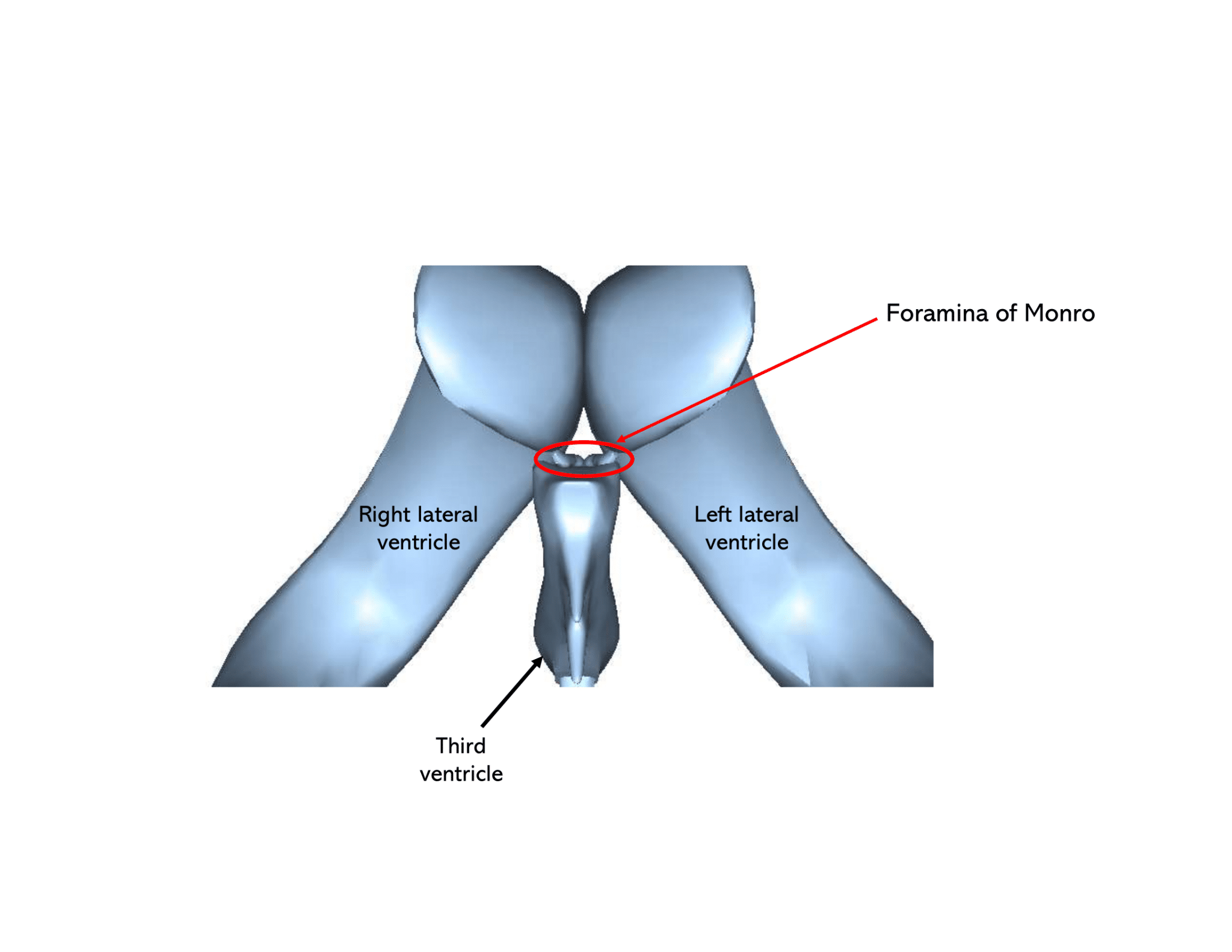
The Ventricular System Neuroanatomy CSF Geeky Medics
Foramen of Monro Fornix Internal Cerebral Vein Posterior Caudate Vein Tela Choroidea Thalamostriate Vein Thalamus Velum Interpositum Interventricular foramen of Monro and roof of the third ventricle. In this axial dissection, rostral is towards the top of the figure and medial is to the left.
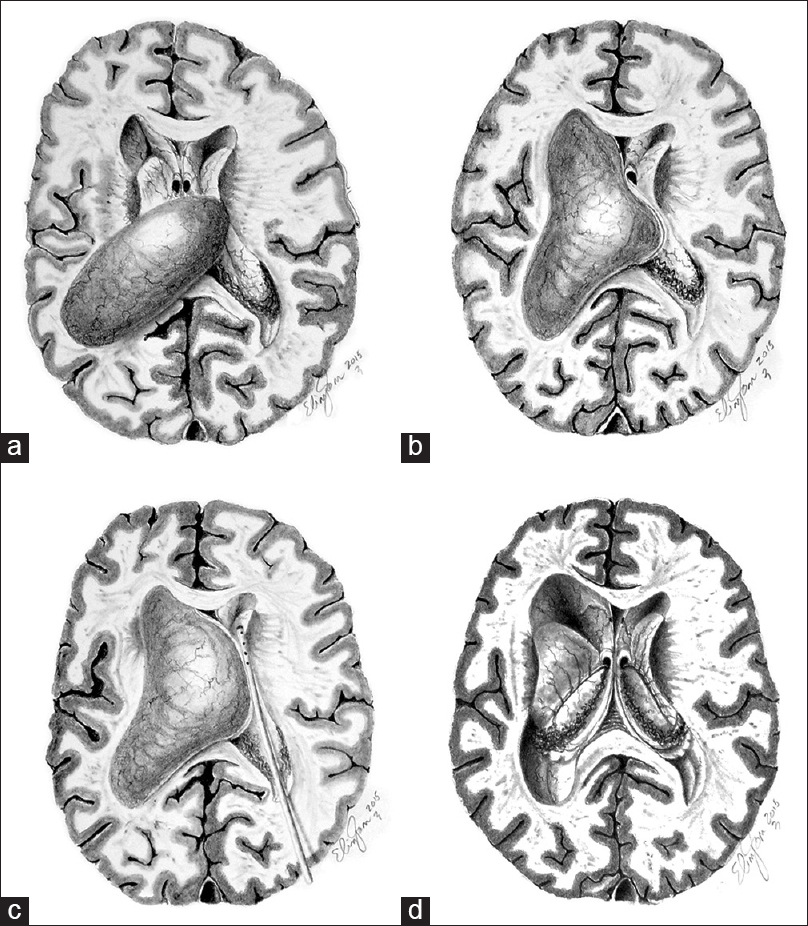
Hydrocephalus caused by unilateral foramen of Monro obstruction A review on terminology
In the brain, the interventricular foramina ( foramina of Monro) are channels that connect the paired lateral ventricles with the third ventricle at the midline of the brain. As channels, they allow cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) produced in the lateral ventricles to reach the third ventricle and then the rest of the brain's ventricular system.

There is a lesion at the level of the foramen of Monro, measuring about... Download Scientific
In 10 cases of foramen of Monro obstruction in children, malignant tumors (5 cases) and postinflammatory occlusions were established as the most common entities. Proper air examination is stressed as the resultant demonstration of the location, extent and nature of the lesions involved was of primary importance in determining treatment. Two cases of unilateral foramen of Monro obstruction with.
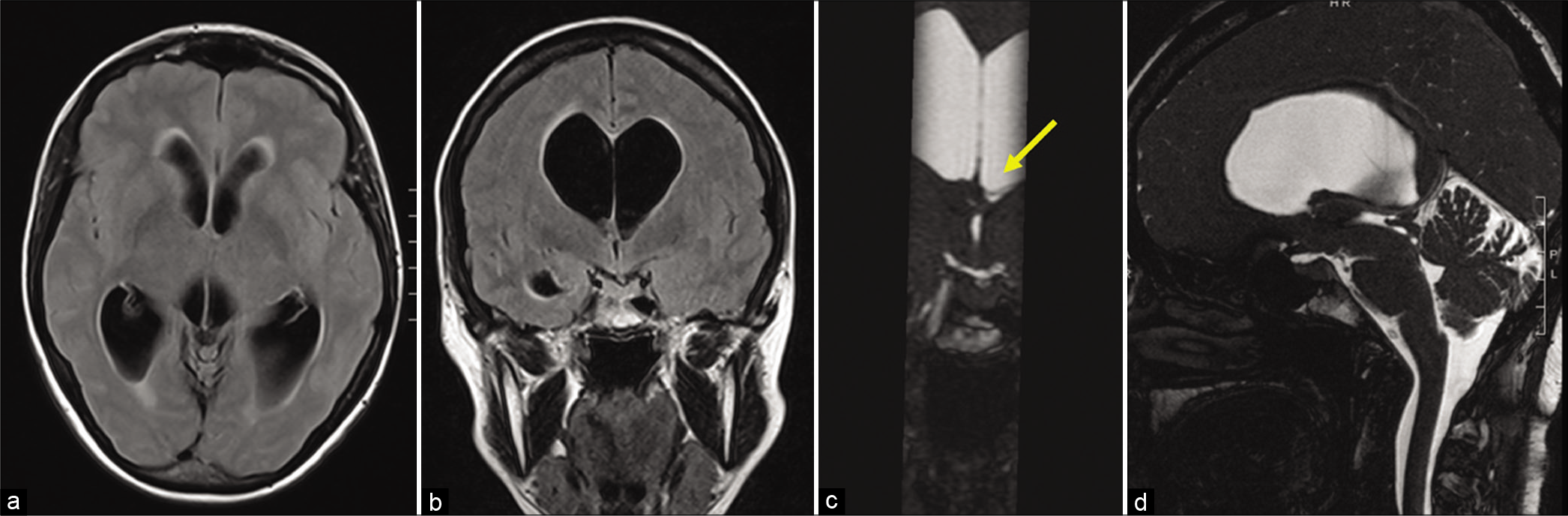
Lateonset occlusion of the Monro foramina after endoscopic third ventriculostomy in adults
Thalamus. Left Interventricular Foramen of Monro. The image is set within the body of the left lateral ventricle. The stria terminalis courses rostrally in the ventrolateral floor of the ventricle in a narrow groove between the body of the caudate and the thalamus. The column of the fornix sweeps inferiorly and posteriorly to form the anterior.

Intraventricular cavernous haemangioma located at the foramen of Monro Eurorad
The foramen of Monro ( Fig. 5.1) is a short conduit connecting the paired lateral ventricles with the third ventricle of the brain. This deep structure becomes clinically significant when obstructed as this leads to obstructive (noncommunicating) hydrocephalus.